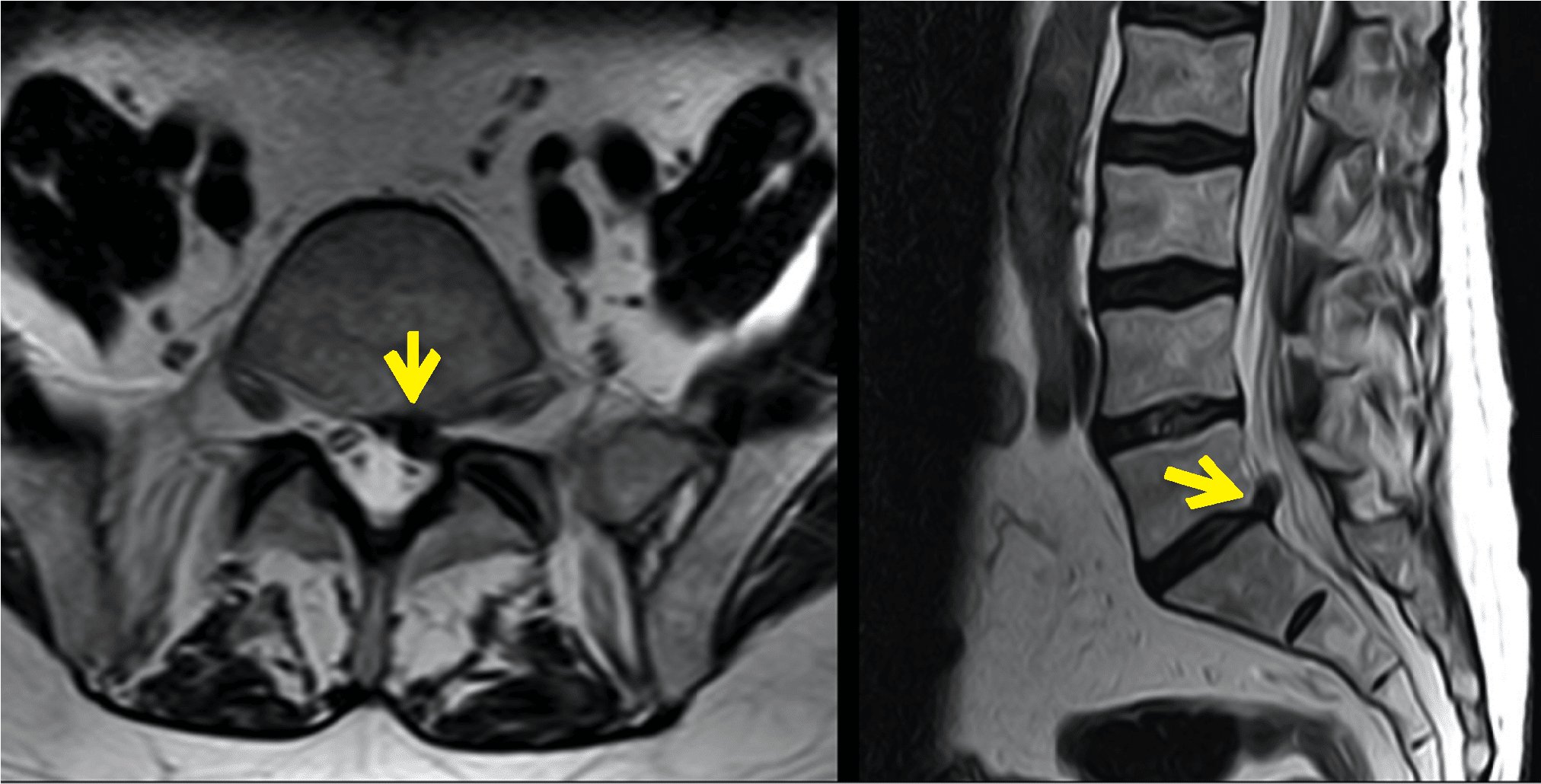
Thecal sac indentation occurs when the protective membrane surrounding the spinal cord is compressed, potentially causing discomfort and nerve-related symptoms. This condition is often detected in various imaging studies, such as MRI scans, and can have different underlying causes. Understanding what thecal sac indentation signifies and its implications is crucial for effective diagnosis and management of related spinal issues. In this article, we delve deeper into what thecal sac indentation entails and explore its significance in spinal health. Let’s unravel the mysteries and shed light on this common spinal concern.
Understanding Thecal Sac Indentation: A Comprehensive Guide
The Basics of thecal sac
Have you ever wondered what thecal sac indentation means? Thecal sac is a protective membrane filled with cerebrospinal fluid that surrounds the spinal cord and nerves within the spinal canal. It plays a crucial role in safeguarding these vital structures from injury and damage.
Exploring Thecal Sac Indentation
Thecal sac indentation occurs when there is pressure exerted on the thecal sac, causing it to compress or deform. This can happen due to various reasons, such as herniated discs, spinal stenosis, or other conditions that result in the narrowing of the spinal canal.
Causes of Thecal Sac Indentation
One common cause of thecal sac indentation is a herniated disc. When the soft inner core of a disc protrudes through the tough outer layer, it can press against the thecal sac, leading to indentation. Another cause is spinal stenosis, which is the narrowing of the spinal canal. This narrowing can put pressure on the thecal sac, causing it to indent.
Symptoms of Thecal Sac Indentation
You might be wondering, what are the symptoms of thecal sac indentation? Well, the symptoms can vary depending on the severity of the indentation and the structures affected. Common symptoms may include pain, numbness, weakness, or tingling sensations in the affected area of the body. In severe cases, thecal sac indentation can lead to complications like bladder or bowel dysfunction.
Diagnosis and Treatment
If you suspect you have thecal sac indentation, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis. Your doctor may recommend imaging tests such as MRI or CT scans to assess the extent of the indentation.
Treatment Options
The treatment for thecal sac indentation depends on the underlying cause and the severity of the condition. It can range from conservative approaches such as physical therapy and pain management to more invasive treatments like surgery to relieve pressure on the thecal sac.
Prevention Tips
While some causes of thecal sac indentation may not be preventable, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk. Maintaining a healthy weight, practicing good posture, and staying physically active can help support spinal health and reduce the likelihood of developing conditions that lead to thecal sac indentation.
In conclusion, thecal sac indentation is a condition that involves the compression or deformation of the protective membrane surrounding the spinal cord and nerves. It can cause a range of symptoms and complications, but with early diagnosis and appropriate treatment, many individuals can find relief and improve their quality of life. If you suspect you have thecal sac indentation, don’t hesitate to seek medical advice to address the issue promptly. Remember, your spine is a vital part of your body, and taking care of it is crucial for your overall well-being.
What is Thecal Sac indentation ? Learn to read MRI
Frequently Asked Questions
What causes thecal sac indentation?
Thecal sac indentation can be caused by various conditions such as disc herniation, spinal stenosis, degenerative changes in the spine, or tumor growth near the spinal canal. These factors can exert pressure on the thecal sac, leading to its indentation.
How is thecal sac indentation diagnosed?
Thecal sac indentation is typically diagnosed through imaging tests like MRI or CT scans. These imaging studies can provide detailed pictures of the spinal structures, allowing healthcare professionals to identify any compression or indentation of the thecal sac.
What are the symptoms of thecal sac indentation?
Common symptoms of thecal sac indentation may include back pain, numbness or weakness in the legs, difficulty walking, and in severe cases, bowel or bladder dysfunction. The specific symptoms can vary depending on the extent and location of the compression on the thecal sac.
Can thecal sac indentation be treated without surgery?
In many cases, thecal sac indentation can be managed through non-surgical treatments such as physical therapy, medications for pain relief, and lifestyle modifications. However, if conservative treatments do not alleviate symptoms or if there is significant nerve compression, surgery may be recommended to decompress the spine and relieve pressure on the thecal sac.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, thecal sac indentation refers to the abnormal narrowing of the thecal sac in the spinal canal. It can result from various conditions like disc herniation or spinal stenosis. This compression can lead to symptoms such as pain, numbness, or weakness in the back and limbs. Understanding theca sac indentation is crucial for diagnosis and determining appropriate treatment.